Types of Brake Testers
2024-07-31
A brake tester is an essential tool used in the automotive industry to evaluate the performance and efficiency of a vehicle's braking system. It provides critical information about the effectiveness, balance, and response of the brakes, ensuring they meet safety standards. Here are the key aspects of brake testers:
Types of Brake Testers
1. Roller Brake Testers
- Function: Measures the braking force by having the vehicle's wheels turn rollers that simulate road conditions.
- Applications: Commonly used in inspection stations and garages for cars, trucks, and buses.
- Features: Provides readings for each wheel separately, indicating any imbalance or inefficiency.
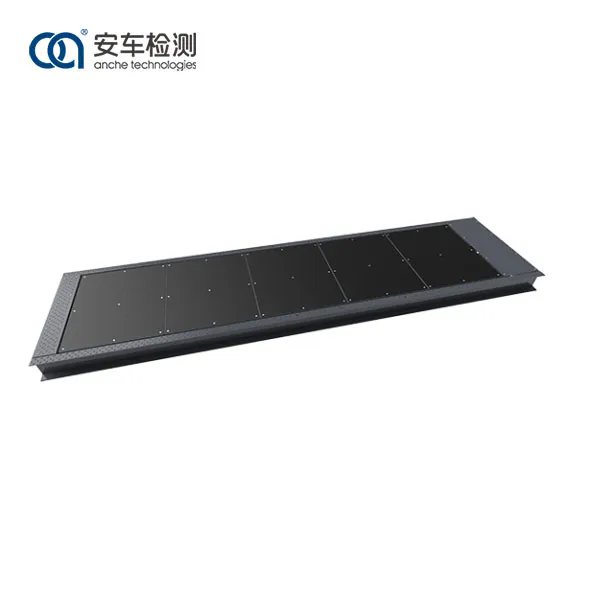
2. Plate Brake Testers
- Function: Measures the braking force as the vehicle drives over a set of plates.
- Applications: Suitable for testing larger vehicles and those with non-standard wheel configurations.
- Features: Often used in commercial vehicle testing due to their ability to handle heavy loads.
3. Decelerometer
- Function: A handheld device that measures the deceleration rate of a vehicle during a braking event.
- Applications: Portable and used for quick checks, particularly for on-road testing.
- Features: Simple to use but may not provide as detailed information as roller or plate testers.
4. Dynamic Brake Testers
- Function: Measures the braking performance under actual driving conditions.
- Applications: Typically used for performance vehicles and in research and development.
- Features: Provides comprehensive data on braking efficiency, including temperature effects and dynamic loading.
Key Features and Metrics
1. Braking Force Measurement
- Indicates the force applied by each brake to ensure they are working correctly and balanced.
2. Imbalance Detection
- Identifies any discrepancies between the braking forces of the left and right wheels, which can lead to uneven braking and potential control issues.
3. Brake Response Time
- Measures the time taken for the brakes to engage after the pedal is pressed, critical for ensuring quick and effective braking.
4. Pedal Force Measurement
- Assesses the force applied to the brake pedal to achieve the desired braking force, ensuring that the brake system responds appropriately to the driver's input.
5. Efficiency and Performance
- Provides an overall assessment of the braking system's efficiency, often expressed as a percentage of the vehicle's weight.
Benefits of Using Brake Testers
- Safety Assurance: Ensures that the vehicle's brakes are functioning correctly, which is crucial for driver and passenger safety.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet safety and performance standards required by automotive regulations.
- Maintenance and Repair: Identifies issues that need attention, aiding in timely maintenance and repairs to prevent brake failure.
- Performance Optimization: Provides data to optimize the braking performance for specific driving conditions or vehicle configurations.
Applications
- Vehicle Inspections: Regular inspections at service stations or during annual vehicle check-ups.
- Fleet Management: Ensures commercial vehicles are safe and roadworthy.
- Research and Development: Used by manufacturers to develop and refine braking systems.
- Performance Tuning: For high-performance or modified vehicles to ensure upgraded brakes meet safety standards.
Summary
Brake testers are crucial tools for ensuring the safety, performance, and regulatory compliance of vehicle braking systems. By providing detailed measurements and diagnostics, they help identify issues, guide maintenance, and optimize braking performance for various applications.